
Polyaspartic Acid (PASP): Mechanism, Benefits, and Applications in Agriculture
Introduction
In modern agriculture, improving fertilizer efficiency and promoting sustainable farming practices are critical. Polyaspartic Acid (PASP) is a green, biodegradable polymer that has gained significant attention for its ability to enhance nutrient uptake, improve soil health, and boost crop productivity. This article explores the science behind PASP, its benefits, and its practical applications in agriculture.
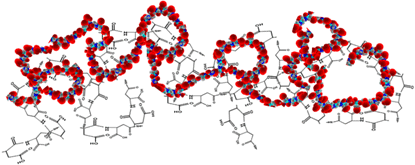
How Does Polyaspartic Acid Work?
Polyaspartic Acid features a unique long-chain structure with numerous carboxyl (–COOH) and amino (–NH₂) groups. These functional groups enable PASP to chelate metal ions in the soil, such as Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, and Fe²⁺, forming soluble complexes. This process prevents nutrients from being fixed by the soil, making them more available to plants.
The chelated nutrients move with water to the root zone, where ion exchange occurs. PASP releases nutrients to the plant roots while exchanging hydrogen ions into the environment, which helps activate and improve soil structure.
Additionally, PASP breaks down into smaller peptides in the environment, each contributing uniquely to plant growth and soil health based on its molecular weight.
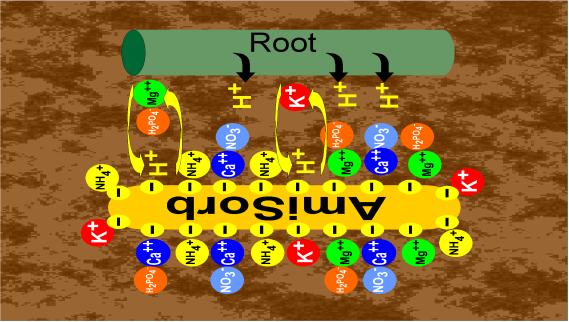
Impact of PASP Molecular Weight on Agricultural Performance
Research shows that the functionality of PASP depends on its molecular weight. Smaller fragments excel in stress resistance, while larger ones improve nutrient transport and soil conditioning.
| Molecular Weight Range | Core Function | Application Effect |
|---|---|---|
| <5000 Da | Stress resistance | Drought/salt tolerance; damage repair |
| 5000–20000 Da | Nutrient chelation | Improves N/P/K efficiency; reduces fertilizer use |
| >20000 Da | Soil structure improvement | Reduces bulk density; increases clay content |
Benefits and Crop Performance
1. Improved Fertilizer Efficiency
PASP significantly enhances nutrient utilization. Field trials conducted by the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences on peanut crops demonstrated that PASP increased nitrogen use efficiency by 60.3%, phosphorus by 5.3%, and potassium by 16.7%. Farmers can reduce fertilizer application by approximately 20% without compromising yield or plant health.
2. Extended Fertilizer Effect
PASP helps maintain higher levels of available nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in the soil throughout the growth cycle. This extended nutrient release supports healthier crops and reduces the risk of nutrient deficiency.
3. Soil Activation
The exchange of hydrogen ions during chelation helps revitalize soil, improving its physical properties and promoting sustainable farming.
Conclusion

Polyaspartic Acid is a powerful tool for enhancing agricultural productivity sustainably. Its ability to improve fertilizer efficiency, support stress resistance, and enhance soil structure makes it an ideal solution for modern farming. For farmers and agricultural suppliers, PASP offers a proven way to reduce costs and support eco-friendly practices.
Yuanlian Chemical specializes in the production of polyaspartic acid (PASP),tetrasodium iminodisuccinate(IDS), GLDA, MGDA etc. with stable quality and excellent quantity!



Contact us