
Maximizing Surfactant Performance: The Essential Role of Chelating Agents in Modern Formulations
In the complex world of chemical formulation, the synergy between surfactants and chelating agents (also known as sequestering agents) is a cornerstone of product efficacy. Whether in industrial cleaning, personal care, or textile processing, understanding this relationship is vital for European formulators aiming to meet high performance standards and stringent environmental regulations.
This article explores the technical mechanisms of chelating agents, their impact on surfactant stability, and the shift toward biodegradable alternatives in the European market.
The Hard Water Challenge: Why Surfactants Need Support
The primary enemy of surfactant efficiency is "hard water"—water containing high concentrations of multivalent metal ions, specifically Calcium () and Magnesium ().
When surfactants, particularly anionic ones, encounter these ions, they often react to form insoluble precipitates, commonly known as "lime soap" or "scum." This reaction leads to:
-
Reduced Detergency: The surfactant is "consumed" by the metal ions, leaving less active material to clean.
-
Poor Aesthetics: Precipitation causes cloudiness in liquid products and leaves residues on surfaces.
-
Reduced Foam: Metal ions interfere with the surfactant’s ability to lower surface tension and create stable foam.
The Mechanism: How Chelating Agents Enhance Performance
Chelating agents act as "chemical claws." They surround and bind to metal ions, forming a stable, water-soluble complex that prevents the ions from interacting with the surfactants.
1. Sequestration and Stability
By sequestering and , chelating agents ensure that the surfactant remains fully available for its intended purpose: emulsifying fats, wetting surfaces, and suspending soils. This synergy allows formulators to use lower concentrations of surfactants while achieving superior cleaning results.
2. Boosting the "Cloud Point"
In non-ionic surfactant formulations, the presence of salts and minerals can lower the cloud point—the temperature at which the mixture begins to phase-separate. Chelating agents help stabilize these systems, maintaining transparency and shelf-life even in fluctuating temperatures.
3. Synergistic Cleaning
Beyond mere protection, some chelating agents contribute to the cleaning process themselves by breaking down calcium-based stains (like limescale) and helping to lift particulate soil from surfaces.
[Image showing surfactant molecules hindered by metal ions vs. protected by chelating agents]
The European Context: The Shift to Green Chemistry
In Europe, the regulatory landscape—governed by REACH and the EU Ecolabel—has significantly influenced the choice of chelating agents. While traditional agents like EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) and NTA are highly effective, their poor biodegradability has led to a surge in demand for "green" alternatives.
Modern, Sustainable Chelants:
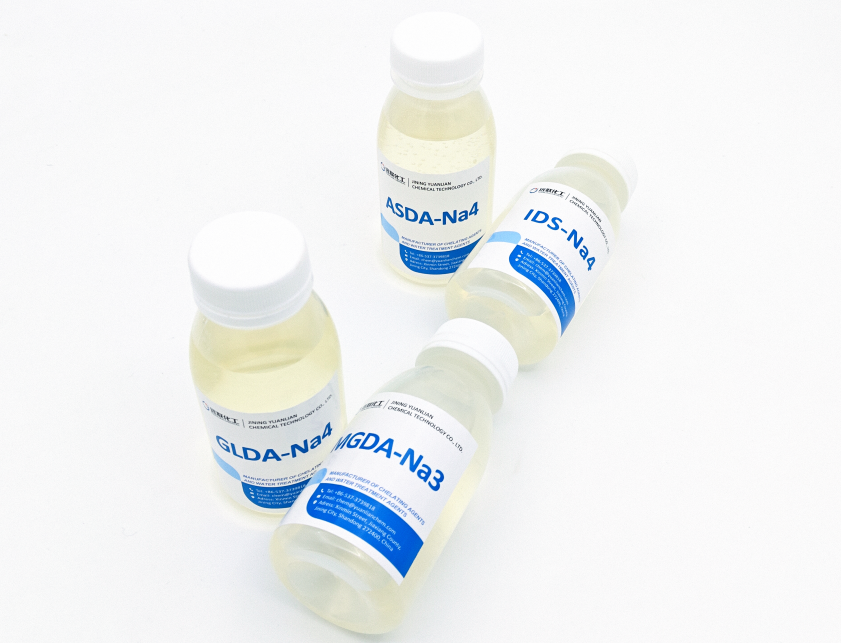

-
GLDA (Tetrasodium Glutamate Diacetate): Derived from natural plant sugars, it offers high solubility and excellent performance across a wide pH range.
-
MGDA (Methylglycinediacetic Acid): Known for its fast-acting sequestration, particularly in high-temperature applications like automatic dishwashing.
-
IDS (Iminodisuccinate): A fully biodegradable option ideal for specialized industrial applications.
These modern chelants are not just "eco-friendly" substitutes; they often provide better solubility and compatibility with concentrated surfactant systems than their legacy counterparts.
Technical Comparison for Formulators
Conclusion: Engineering Better Solutions
The integration of high-performance chelating agents is no longer optional for premium European brands; it is a technical necessity. By protecting surfactants from the interference of metal ions, chelators ensure cost-effectiveness, visual clarity, and peak performance of the final product.
As we move toward a circular economy, the transition to biodegradable chelants like GLDA and MGDA represents the gold standard for innovation in chemical manufacturing.
Yuanlian Chemical specializes in the production of polyaspartic acid (PASP),tetrasodium iminodisuccinate(IDS), GLDA, MGDA etc. with stable quality and excellent quantity!



Contact us