
Beyond EDTA: Embrace High-Performance & Eco-Friendly Chelation with GLDA, MGDA, and IDS
The Legacy of EDTA: A Double-Edged Sword
For over half a century, EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) has dominated industrial chelation. Its ability to bind metal ions like calcium, iron, and heavy metals made it indispensable in wastewater treatment, detergents, agriculture, and textiles. However, EDTA’s environmental footprint is now under global scrutiny:
-
Persistent Pollution: EDTA resists biodegradation, accumulating in ecosystems for decades.
-
Toxic Remobilization: It binds to buried heavy metals (e.g., lead, cadmium), forming soluble complexes that contaminate groundwater.
-
Phosphorus Burden: Common EDTA salts contain phosphorus, accelerating eutrophication in aquatic systems.
-
Health Risks: Linked to allergic reactions and false medical diagnostics (e.g., pseudothrombocytopenia).
With regulations tightening worldwide, industries urgently need EDTA-free solutions that match performance without ecological harm.
The Green Revolution: GLDA, MGDA, and IDS
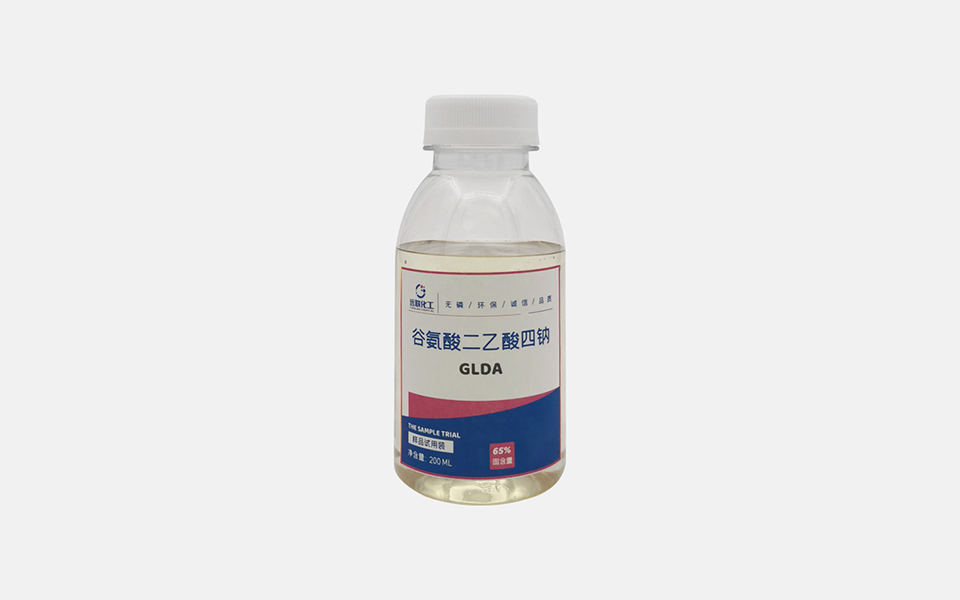
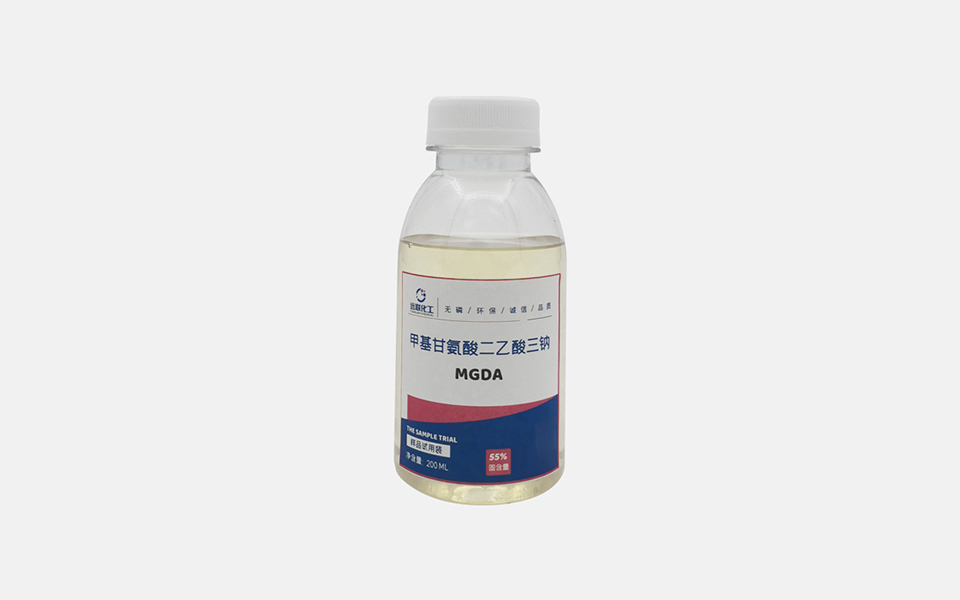
Meet the next-generation chelators—GLDA (Tetrasodium Glutamate Diacetate), MGDA (Trilayer Trisodium Methylglycinediacetate), and IDS (Tetrasodium Iminodisuccinate). These innovations deliver EDTA-level efficacy while aligning with circular economy principles.
✅ 1. GLDA: The Biodegradable Powerhouse
-
Origin: Plant-derived (e.g., fermented glutamic acid), renewable and sustainable
-
Performance: Near-identical calcium binding efficiency to EDTA, superior to citrates and phosphonates.
-
Applications:
-
Household & industrial detergents (removes stubborn stains without phosphorus).
-
Textile dyeing (prevents metal ion interference for vibrant colors).
-
Soil remediation (extracts heavy metals without persistence).
-
-
Eco-Advantage: >60% biodegradability in 28 days (OECD 301D).
✅ 2. MGDA: The Versatile Degrader
-
Strength: High solubility and stability across pH levels (1–14), ideal for harsh formulations.
-
Applications:
-
Automatic dishwashing (replaces phosphates, prevents scale).
-
Dairy equipment cleaning (dissolves calcium phosphate without corrosion).
-
Oilfield chemicals (compatible with high-salinity environments).
-
-
Eco-Advantage: Fully biodegradable, no aquatic toxicity.
✅ 3. IDS: The Multi-Metal Champion
-
Award-Winning: 2001 U.S. Presidential Green Chemistry Award.
-
Performance: Outperforms EDTA in binding transition metals (e.g., iron, copper).
-
Applications:
-
Agriculture (enhances micronutrient uptake in crops, 100% metabolizable).
-
Water treatment (prevents scaling without sludge formation).
-
-
Eco-Advantage: Rapid biodegradability, zero phosphorus
Why Choose Green Chelators Over EDTA?
| Factor | EDTA | GLDA/MGDA/IDS |
|---|---|---|
| Biodegradability | Non-degradable (persists >80 years) | >60% in 28 day |
| Phosphorus Content | High (eutrophication risk) | Zero phosphorus |
| Metal Management | Remobilizes toxic metals | Stabilizes/removes metals sustainably |
| Regulatory Status | Restricted in EU/NA markets | Compliant with REACH/EPA standards |
Future-Proof Your Industry
Regulations are shifting: EDTA is phased out in the EU for detergents, while China’s “Dual Carbon” policy prioritizes biodegradable alternatives45. Brands like AkzoNobel (Dissolvine® GL) and Desai Chemical (IDS) lead the transition with industrial-scale production
Case Study: A textile manufacturer replaced EDTA with GLDA, reducing wastewater COD by 40% while maintaining dyeing quality—proving sustainability enhances profitability.
Conclusion: The EDTA Era Ends Here
EDTA paved the way—but its legacy is ecological debt. With GLDA, MGDA, and IDS, industries gain:
-
♻️ Zero persistence: Safeguard water/soil health.
-
Yuanlian Chemical specializes in the production of polyaspartic acid (PASP),tetrasodium iminodisuccinate(IDS), GLDA, MGDA etc. with stable quality and excellent quantity!





Contact us